Abstract
Although several effective therapies are available for Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), new treatments are needed, especially for chemotherapy-refractory HL. We developed a novel anti-CD30 CAR, designated 5F11-28Z, with a human antibody-derived binding domain, CD28 hinge, transmembrane, and costimulatory domains, and a CD3-ζ domain (Choi et al., Hum Gene Ther 2021; 32(13-4): 730-43). T cells expressing 5F11-28Z are designated 5F11-28Z-T; 5F11-28Z-T exhibited a full range of T-cell functions in vitro and eradicated tumors from mice. Safety and feasibility of 5F11-28Z-T were evaluated in a phase I clinical trial for patients (Pts) with CD30-expressing lymphomas (NCT03049449).
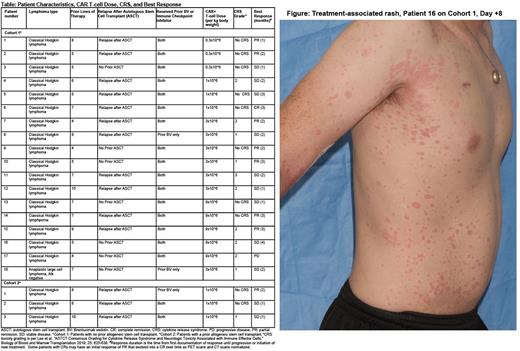
Pts were divided into 2 cohorts with separate dose escalations based on prior allogeneic stem cell transplant status and received 5F11-28Z-T on one of 4 dose levels (Table). The treatment protocol was 300 mg/m2 or 500 mg/m2 of cyclophosphamide and 30 mg/m2 of fludarabine on days -5 to -3 followed by infusion of 5F11-28Z-T on day 0. Normal organ function and absence of baseline Grade (Gr) 3-4 cytopenias were required for eligibility.
Twenty-one Pts received 5F11-28Z-T infusions, 20 with HL and 1 Pt with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Table). The median prior lines of therapy was 7 (4-15). Forty-three percent of Pts (9 of 21) obtained a response of partial remission or better with one (4.8%) obtaining a complete remission. The median event-free survival was 13 (4-22) weeks.
Eleven Pts (52%) had cytokine release syndrome (CRS): 4 (19%) with Gr 1, 6 (29%) with Gr 2, 1 (4.8%) with Gr 3, and no Pts had grade 4-5. Two Pts (9.5%) received tocilizumab; no Pts received corticosteroids for CRS. Neurologic toxicity possibly related to CAR T cells (graded by CTCAE v 5) occurred at Gr 2 in 5 (24%) Pts, with no Gr 3-4 events. There were no treatment related deaths.
Nine Pts (43%) had new onset maculopapular or pustular rashes after 5F11-28Z-T infusion (Figure). Rashes occurred a median of 11 (7-55) days after 5F11-28Z-T infusion and lasted at Gr of 2 or higher for a median of 7 (3-39) days. Six Pts had Gr 2 rashes; 3 Pts had Gr 3 rashes. Two Pts with Gr 3 rashes lasting 29 and 39 days received systemic corticosteroids for management of rash. One Pt received phototherapy.
Nineteen Pts (90%) had Gr 3-4 neutropenia; 5 (24%) had Gr 3-4 thrombocytopenia; and 6 (29%) had Gr 3-4 anemia. Three Pts (14%) had Gr 3-4 cytopenias lasting more than 30 days. Two Pts had prolonged pancytopenia, lasting 77 and > 82 days; both Pts had infections requiring intensive care while neutropenic. Three Pts received eltrombopag; 2 Pts received corticosteroids for management of prolonged cytopenias. Eleven bone marrow (BM) biopsies were performed for 5 Pts to evaluate cytopenias. All biopsies showed hypocellularity; 10/11 (4 Pts) showed trilineage or myeloid hypoplasia, 4/11 (2 Pts) showed fibrosis, 1 showed stromal gelatinous changes, and none showed HL or dysplasia.
Blood 5F11-28-T were detected in all 15 patients assessed so far. A median of 2.2% (range 0.1-29.4%) of peripheral blood mononuclear cells contained the CAR gene. An immunohistochemical stain for CAR+ cells was performed with an antibody against the CAR linker. Seven Pts had technically adequate tumor biopsies within 30 days following 5F11-28Z-T; infiltrating CAR+ cells were not detected in any of these biopsies. For comparison, post-treatment tumor biopsy specimens from Pts with B-cell lymphoma were collected within 30 days after infusion of anti-CD19 CAR T-cells (Brudno et al., Nat Med 2020; 26: 270-80). These specimens were stained for CAR+ cells with the same antibody used to stain for 5F11-28Z-T. Two of 5 Pts (40%) had one or more tumor biopsy samples with detectable CAR+ cells. Four Pts with rashes after 5F11-28Z-T had skin biopsies, which showed a spongiotic dermatitis. CD30 was detected on mononuclear cells in 2 biopsies (2 Pts). Of 3 evaluable skin biopsies, 1 performed at Day 7 had detectable CAR+ cells in the dermis; none from later time points had CAR+ cells. Three Pts with Gr 4 cytopenias had 5 evaluable BM biopsies after 5F11-28Z-T. The earliest biopsy, performed at Day 16, had CAR+ cells.
In conclusion, 5F11-28Z-T cells have limited anti-malignancy efficacy. Severe toxicities from rashes and myelosuppression may be due to CD30 expression on dermal mononuclear cells and on hematopoietic stem cells (Hombach et al., Mol Ther 2016; 24(8):1423-34). These toxicities along with limited anti-lymphoma activity prompted us to end this clinical trial.
Disclosures
Brudno:Kyverna Therapeutics, Inc.: Other: unpaid member of scientific advisory board. Lam:Kite, a Gilead Company: Patents & Royalties. Kochenderfer:Bristol Myers Squibb: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Kyverna Therapeutics, Inc: Patents & Royalties.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Anti-CD30 CAR T cells were given to participants of a clinical trial. Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide were given prior to CAR T cells as off-label use.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal